Sentencing
This page will outline the different types of sentence and how a court makes a decision about sentence.
The purpose of sentencing is:
a) the punishment of offenders;
b) the reduction of crime;
c) the reform and rehabilitation of offenders;
d) the protection of the public; and
e) the making of reparation by offenders to the persons affected by their offenceds.
Deciding A Sentence
Sentening Guidelines
The Courts of the Falkland Islands apply the Setencing Guidelines issued by the Sentencing Council of England and Wales.
Overarching Sentencing Guideline
The Sentencing Guidelines Committee of the Falkland Islands has issued an Overarching Sentencing Guideline. This Guideline is applied by the Courts of the Falkland Islands when deciding upon sentence.
Enforcement or Breach of a Sentence
If you fail to comply with a sentence, you may be summonsed to appear back before the court for either enforcement action or breach proceedings.
Fines Enforcement
If you fail to pay a financial penalty as ordered, the court will summons you to appear before it and explain why you have failed to make payment. Enforcement may include:
- vary the terms of payment; or
- revoke the financial order and re-sentence you; or
- make an attachment of earnings order; or
- issue a distress warrant; or
- order that you serve a term of imprisonment for non-payment.
If you are unable to pay as you have been ordered, you should contact the court office as soon as possible.
Breach Proceedings
If you breach a community order or a suspended sentence supervision sentence, you will be summonsed back before the court. If the court is satisfied that you have, without reasonable excuse, failed to comply with any of the requirements of your community order it may:
- impose more onerous requiements onto your community order; or
- re-sentence you for the original offence.

Sentencing Options
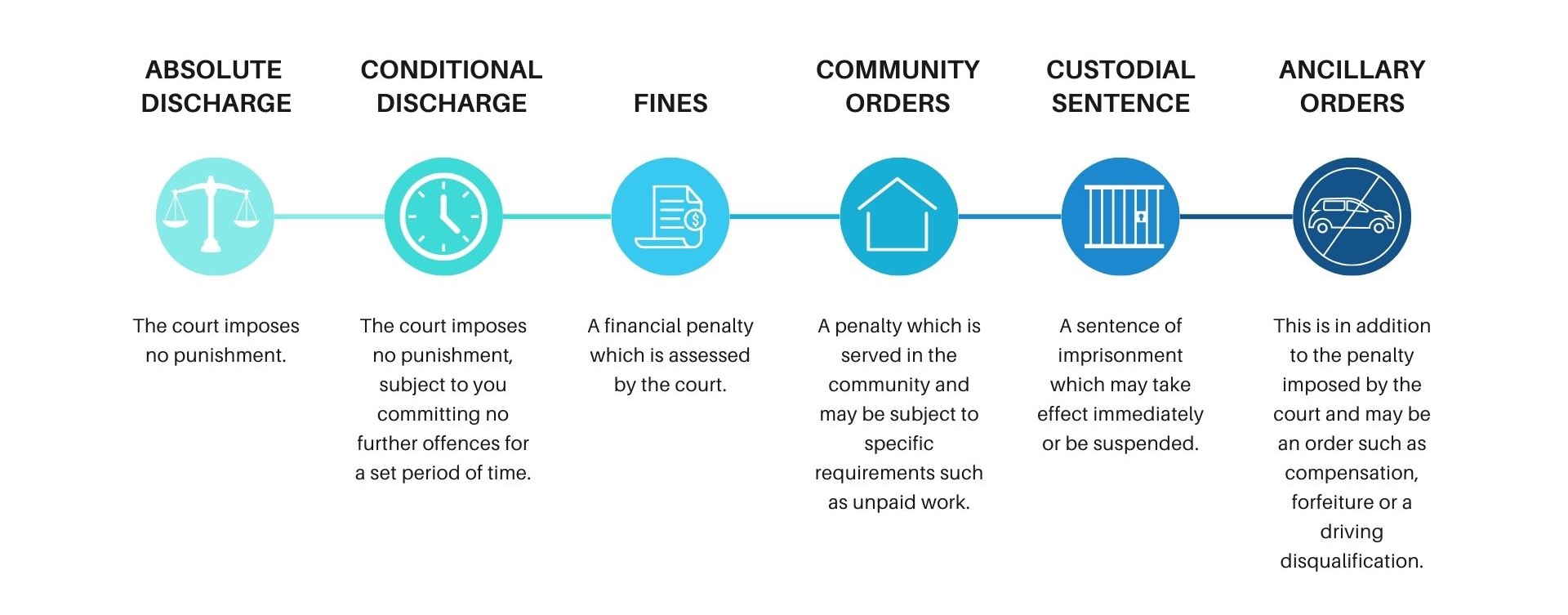
Discharges
There are two types of a discharge options available to a court.
Absolute Discharge: If, having looked at all the cirucmstances of the offence and your characteristics, the court may decide to give you an absolute discharge. This means you will be convicted of the offence but there is no additional punishment.
Conditional Discharge: If, having looked at all the cirucmstances of the offence and your characteristics, the court may decide to give you an absolute discharge. This means you will be convicted of the offence but there is no additional punishment unless you are convicted of another offence within a set period of time. If you are convicted of a further offence, you may be sentenced for the orginal offence and the further offence.
Fines
The court may impose a financial penalty (a fine). The Summary Court may impose a fine up to a maximum of £5,000. The Magistrate's Court and the Supreme Court have no limit to their fining powers.
If the court are considering imposing a financial penalty, you will be asked to complete a means form. The court will take your financial circumstances into consideration when applying the Sentencing Guidelines to your offence. A financial penalty is based upon your weekly income. More information about the fine bands is available here.
How to pay
There are 3 ways you may pay your financial penalty:
1) In person at the court office with cash or local cheque; or
2) Standard Chartered local bank transfer; or
3) UK bank transfer
You will find further information on your Notice of Sentence. If you require any further assistance regarding your financial penalty, please contact the court office.
Community Orders
A community order is a sentence which is carried out whilst you are a part of the community. A coomunity order may require you to undertake one or more of the following requirements:
- an unpaid work requirement
- an activity requirement
- a programme requirement
- a prohibited activity requirement
- a curfew requirement
- an exclusion requirement
- a residence requirement
- a foreign travel prohibition requirement
- a mental health treatment requirement
- a drug rehabilitation requirement
- an alcohol treatment requirement
- an alcohol abstinence and monitoring requirement
- an intoxicating substance treatment requirement
- a supervision requirement
- an electronic monitoring requirement.
Before a court imposes a community order, it will likely seek a Pre-Setence Report from the Probation Officer. You will be required to attend meetings with the Probation Officer to facilitate this report. If the court imposes a community order, any additional requirements will be tailored to what the Probation Service is able to provide and support, and what will best acheive the aims of sentencing.
Custodial Sentence
The court may decide that the offence is so serious that only a custodial sentence is appropriate. If this is the case, it is likely the court will request a Pre-Sentence Report from the Probation Officer. You will be required to attend meetings with the Probation Officer to facilitate this report.
If the court imposes a custodial sentence it may order for the sentence to take immediate effect, or it may suspended the sentence for up to two years. If your custodial sentence is to take effect immediately, you will be taken into custody in the court and taken to HMP Stanley from there. You will be eligible for release after serving two-thirds of your sentence.
Suspended Sentences: if your sentence is not more than 2 years imprisonment, the court may suspended your sentence. That means you will not be taken into custody unless you commit a further offence within a set period of time (known as 'the operational period').
Suspended Sentence Supervision Order: if the court imposes a suspended sentence it may make a suspended sentence supervision order. This means that you are placed under the supervision of the Probation Officer. The court may also attach any of the following requirements to the supervision order which seem appropriate to acheiving the aims of sentencing:
- an unpaid work requirement
- an activity requirement
- a programme requirement
- a prohibited activity requirement
- a curfew requirement
- an exclusion requirement
- a residence requirement
- a foreign travel prohibition requirement
- a mental health treatment requirement
- a drug rehabilitation requirement
- an alcohol treatment requirement
- an alcohol abstinence and monitoring requirement
- an intoxicating substance treatment requirement
- a supervision requirement
- an electronic monitoring requirement.
As with a suspended sentence, the period of imprisonment will not take effect unless you commit a further offence with the operational period of the order.
Ancillary Orders
An ancillary order is not the punishment. It is an order the court imposes in addition to the sentence. Examples of ancillary orders include:
- Driving Disqualification
- Sexual Harm Prevention Orders
- Forfeiture Orders
- Compensation
- Restitution Order
